Transfusions are “the only evidence-based option to prevent stroke recurrence and further brain injury in this vulnerable population,” said the study’s co-author Michael Noetzel, a professor of neurology and of pediatrics at Washington University. “Now that we have identified a viable treatment option, early detection of silent cerebral strokes should become a major focus for clinicians and families of children with sickle cell disease.”
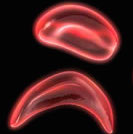
Sickle cell disease affects about 100,000 people in the United States and occurs most commonly in African-Americans. The disease, inherited from both parents, causes some of the patient’s red blood cells, normally shaped like a saucer, to take on a crescent or sickle shape. These malformed cells are less effective at their primary job, conveying oxygen from the lungs to the rest of the body. The cells also clump together, blocking circulation and leading to organ damage, strokes and episodes of intense pain.
The research, “Controlled Trial of Transfusions for Silent Cerebral Infarcts in Sickle Cell Anemia,” was published in the August 21 issue of the New England Journal of Medicine. It may be accessed here.

